The Immune System
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. The immune system is essential for maintaining overall health and wellbeing, as it helps prevent infection and disease.
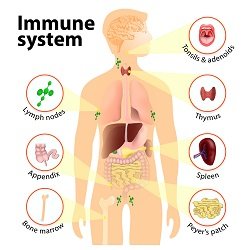
The immune system is made up of several different components, including white blood cells, antibodies, and the lymphatic system. White blood cells are responsible for identifying and destroying harmful invaders, while antibodies are proteins that help neutralize harmful substances in the body. The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and tissues that helps circulate immune cells throughout the body.
There are two main types of immunity: innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity is the body’s first line of defense against harmful invaders, and it includes physical barriers, such as the skin and mucous membranes, as well as specialized cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages. Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, is a more specific and targeted response that develops over time in response to exposure to specific invaders. Adaptive immunity includes the production of antibodies and the activation of specialized immune cells, such as T cells and B cells.
The immune system can sometimes malfunction, leading to autoimmune disorders, in which the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues and organs. Examples of autoimmune disorders include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis.
There are several factors that can affect the immune system, including age, stress, diet, and lifestyle factors. As people age, their immune system may become less effective, making them more susceptible to infection and disease. Stress can also affect the immune system, as chronic stress can lead to a weakened immune response. A healthy diet and lifestyle can help support a healthy immune system, as can regular exercise and adequate sleep.
The immune system is also responsible for recognizing and destroying abnormal cells, such as cancer cells, before they can develop into tumors. However, cancer cells can sometimes evade the immune system, allowing tumors to grow and spread.
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that works by stimulating the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Immunotherapy has shown promise in treating several types of cancer, including melanoma, lung cancer, and bladder cancer.
Vaccines are another important tool in the fight against disease. Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against specific invaders, such as viruses and bacteria. This helps prevent infection and can even lead to the eradication of certain diseases, such as smallpox.
However, vaccines can sometimes be controversial, with some people questioning their safety and efficacy. It’s important to note that vaccines undergo rigorous testing and are considered safe and effective by the medical community. Vaccines have been instrumental in preventing the spread of infectious diseases and have saved countless lives.
Overall, the immune system is a complex and essential component of overall health and wellbeing. By defending the body against harmful invaders, the immune system helps prevent infection and disease, and plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and wellbeing.
How it protects body from diseases and infections
The immune system protects the body from disease and infection by identifying and destroying harmful invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. The immune system is made up of several different components, including white blood cells, antibodies, and the lymphatic system.
White blood cells are responsible for identifying and destroying harmful invaders, while antibodies are proteins that help neutralize harmful substances in the body. The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and tissues that helps circulate immune cells throughout the body.
When an invader enters the body, such as a virus or bacteria, the immune system responds by producing specific antibodies and activating specialized immune cells, such as T cells and B cells. These immune cells work together to identify and destroy the invader, helping prevent infection and disease.
The immune system is also responsible for recognizing and destroying abnormal cells, such as cancer cells, before they can develop into tumors. However, cancer cells can sometimes evade the immune system, allowing tumors to grow and spread.
In addition to identifying and destroying harmful invaders, the immune system also plays a role in inflammation and wound healing. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, and helps to protect the body from further damage. The immune system helps to regulate inflammation, ensuring that it is not excessive or prolonged, which can lead to tissue damage and chronic disease.
The immune system can also be influenced by a variety of factors, including diet, exercise, stress, and sleep. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can all help support a healthy immune system, while chronic stress and unhealthy lifestyle habits can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of infection and disease.
Certain medical conditions and medications can also affect the immune system. For example, autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the body, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Medications such as chemotherapy and immunosuppressants can also weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infection and disease.
In conclusion, the immune system is a complex and essential component of overall health and wellbeing. It protects the body from disease and infection by identifying and destroying harmful invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. The immune system also plays a role in inflammation and wound healing, and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including diet, exercise, stress, and sleep. By understanding how the immune system works and how it can be supported, we can take steps to maintain overall health and wellbeing.